ISRO 3D Printed Rocket Engine: Latest Triumph in Space Innovation
- saugatadastider
- May 25, 2024
- 18 min read
May 10th 2024: ISRO has successfully conducted a long-duration test of its PS4 engine, re-designed for production using cutting-edge additive manufacturing (AM) techniques

Table of Contents
Introduction.
Section 1: ISRO's 3D Printed Rocket Engine.
1.1 Overview of the 3D Printed Rocket Engine.
1.2 Development and Testing.
Section 2: Contributions from AgniKul and Skyroot.
2.1 AgniKul Background and Achievements.
2.2 Skyroot Background and Achievements.
2.3 Launch Vehicles: Details About AgniKul and Skyroot’s Launch Vehicles.
Contributions to India’s Space Missions.
Section 3: Applications and Future Plans of 3D Printing by ISRO.
3.1 Current Applications: Other Areas Where ISRO is Using 3D Printing.
3.2 Future Applications: Future Plans for 3D Printing in Space Exploration.
Potential Advancements and Innovations
Section 4: Comparison and Challenges in Additive Manufacturing.
4.1 ISRO vs. Other Space Agencies.
4.2 Challenges in Large-Scale 3D Printing.
How ISRO is Addressing These Challenges.
Section 5: Future Prospects and Developments in India.
5.1 Recent Developments in 3D Printing Technology in India.
5.2 Future Scopes and Projects.
Applications of 3D Printing in Other Industries in India.
Conclusion.
Introduction
In recent years, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has achieved remarkable milestones, showcasing India's growing capabilities in space technology. Here’s a brief overview of some of these significant achievements:
ISRO's Chandrayaan 3.0: India's Bold Lunar Adventure in Space: Chandrayaan-3 successfully landed near the moon's south pole with minimal moon dust disruption, marking a significant achievement in lunar exploration.
ISRO’s Aditya L1 Solar Space Mission: Aditya-L1 is India's first dedicated solar mission, positioned in a halo orbit around the Sun-Earth Lagrange point 1 (L1) to ensure continuous solar observation.
ISRO Gaganyaan Mission: Pioneering Crewed Space Journey: Gaganyaan is India's inaugural crewed space mission, aiming to send a three-member crew on a journey lasting five to seven days, with a primary focus on their safe return.
ISRO's POEM-3 Triumph: Zero Orbital Debris Mission: The PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-3 (POEM-3) mission re-entered Earth's atmosphere without leaving any orbital debris, showcasing ISRO’s commitment to sustainable space exploration.
Adding a new feather to its cap, ISRO has successfully tested a 3D printed rocket engine, a significant breakthrough in space technology. This engine, developed with the help of Wipro's 3D printing companies, marks a major advancement in additive manufacturing, which can revolutionize the space industry by reducing costs, increasing production speed, and allowing for the creation of complex, customized components.
This achievement aligns perfectly with the Atmanirbhar Bharat Mission, which aims to make India self-reliant and technologically advanced. By leveraging domestic R&D and innovation, ISRO continues to lead the way in space exploration, demonstrating the immense potential of Indian industries.
In this article, we will explore the following:
Details of ISRO's 3D printed rocket engine and its future plans.
Contributions and achievements of Indian startups AgniKul Cosmos and Skyroot Aerospace.
Applications and future prospects of 3D printing technology in space exploration.
A comparison of ISRO's advancements in additive manufacturing with other space agencies and the challenges faced in large-scale 3D printing.
Join us as we delve into these exciting developments, celebrating ISRO's ongoing journey of innovation and excellence.
Section 1: ISRO's 3D Printed Rocket Engine

1.1 Overview of the 3D Printed Rocket Engine
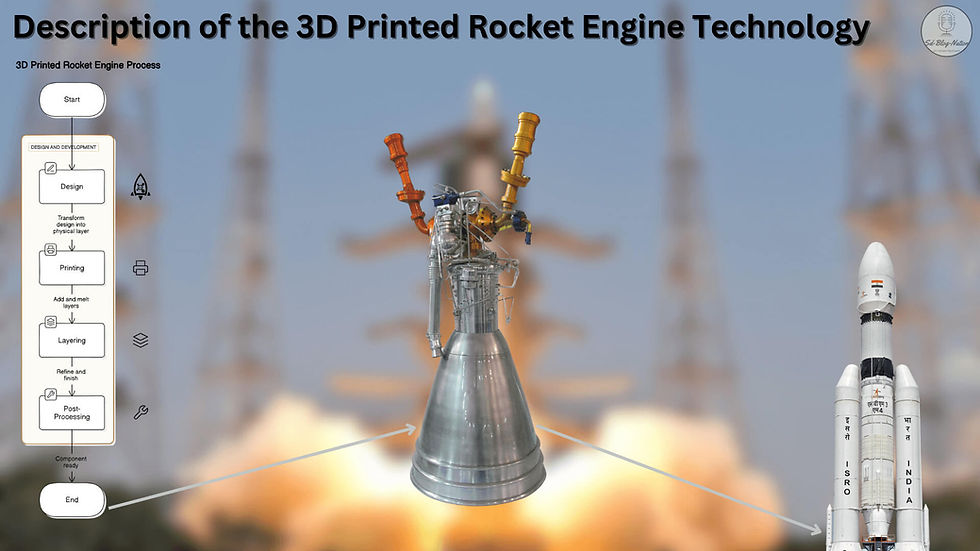
In the world of space exploration, innovation is the key to pushing boundaries and achieving new heights. ISRO's recent success in testing a 3D printed rocket engine is a testament to India's commitment to leveraging cutting-edge technology for its space missions.
Description of the Technology
The process of 3D printing rocket engines, also known as additive manufacturing, represents a transformative approach in aerospace engineering. Here's a closer look at this groundbreaking technology:
Design: The journey begins with a digital 3D model of the rocket engine component, crafted using advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software. This digital model allows engineers to optimize the design for specific mission requirements and make modifications with ease.
Printing: Using a 3D printer, the component is built layer by layer from the bottom up. This process involves depositing material, usually metal powder, onto a build plate. A laser or electron beam then precisely melts the powder to form the current layer of the component.
Layering: The build plate is lowered, and a new layer of powder is spread on top. This layering process is repeated until the entire component is constructed, resulting in a highly detailed and complex structure.
Post-Processing: Once printing is complete, the component undergoes various post-processing steps, including heat treatment to relieve stresses built up during printing and machining to achieve the final dimensions and surface finish.
The advantages of 3D printed rocket engines are numerous:
Complexity and Precision: This technology allows for the production of components with intricate geometries that are challenging to achieve with traditional methods, leading to more efficient and effective engine designs.
Speed and Cost Efficiency: The production process is significantly faster, and material waste is minimized, resulting in substantial cost savings.
Customization: 3D printing enables easy customization, allowing engines to be tailored to meet specific mission requirements.
ISRO's 3D printed rocket engine, now a single piece, saves an impressive 97% of raw materials and reduces production time by 60%. This achievement not only highlights the technological prowess of ISRO but also demonstrates the immense potential of 3D printing in the space industry.
Importance of Additive Manufacturing in Space Technology

Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, holds significant importance in the realm of space technology. Here are some key reasons why:
Complexity and Precision: The ability to produce parts with complex geometries ensures more efficient and effective designs, crucial in space technology where precision is paramount.
Speed and Cost Efficiency: Accelerating the production process and reducing material waste lead to significant cost savings, an essential factor in the high-cost space industry.
Customization: Components can be easily customized for specific mission requirements, providing flexibility and adaptability for various space missions.
On-Demand Manufacturing: 3D printing allows for the production of parts as needed, reducing the need for large inventories and enabling timely solutions during long-duration space missions.
In-Space Manufacturing: The future potential of 3D printing includes manufacturing parts in space using locally sourced materials, reducing dependence on Earth-based resources and lowering launch costs.
In summary, additive manufacturing has the potential to revolutionize space technology, making it more efficient, cost-effective, and adaptable. This promising area is paving the way for the future of space exploration.
Reference to ISRO’s Tweet About the Breakthrough
ISRO recently celebrated this technological breakthrough with an official tweet:
This tweet underscores the significance of ISRO's achievement, marking a new era in India's space exploration endeavors through innovative additive manufacturing techniques.
1.2 Development and Testing
Role of Wipro's 3D Printing Companies

Wipro 3D, a division of Wipro Infrastructure Engineering, played a crucial role in the development of ISRO's 3D printed rocket engine. Here are some key points:
Manufacturing: Wipro 3D was responsible for the manufacturing of the additively manufactured engine. The engine was built using a technique called Laser Powder Bed Fusion.
Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM): Wipro 3D helped in redesigning the PS4 engine to make it compatible with additive manufacturing techniques. This innovative approach, known as Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM), has yielded remarkable advantages.
Advantages: The redesign resulted in considerable savings in raw material usage per engine. Specifically, it reduced metal powder usage from 13.7 kg to 565 kg of forgings and sheets in conventional manufacturing processes. Moreover, the overall production time was slashed by 60% due to this redesign.
Made-in-India Achievement: The engine was built by Wipro 3D, an Indian company that is part of the well-known corporation Wipro. This marked a significant 'Made-in-India' achievement, aligning with the Aatmanirbhar Bharat mission's goal of promoting domestic industries and reducing dependence on foreign technologies.
These efforts demonstrate Wipro 3D's commitment to innovation and its significant contribution to India's space exploration efforts.
Details of the Successful Long-Duration Test

The successful long-duration test of ISRO's 3D printed rocket engine, known as the PS4 engine of PSLV upper stage, was a significant milestone. Here are some key details:
The hot testing of the engine was conducted on May 9, 2024.
The test lasted for 665 seconds (11 minutes 5 seconds).
As part of the development process, the injector head of the engine was realized and successfully hot-tested earlier.
Detailed flow and thermal modeling, structural simulation, and cold flow characterization of the proto hardware were carried out to gain confidence for the hot test.
Four successful developmental hot tests of the integrated engine were conducted previously for a combined duration of 74 seconds. These combined tests validated the engine performance parameters.
Thereafter, the engine was successfully tested for the full qualification duration of 665 seconds.
Upon testing, it was observed that all performance parameters were as expected.
It is planned to induct this AM PS4 engine into the regular PSLV program.
This successful test opens up possibilities for advanced manufacturing techniques in India's space program. It's indeed a significant step in leveraging additive manufacturing technology for rocket engines in the future.
Future Plans for the 3D Printed Rocket Engine
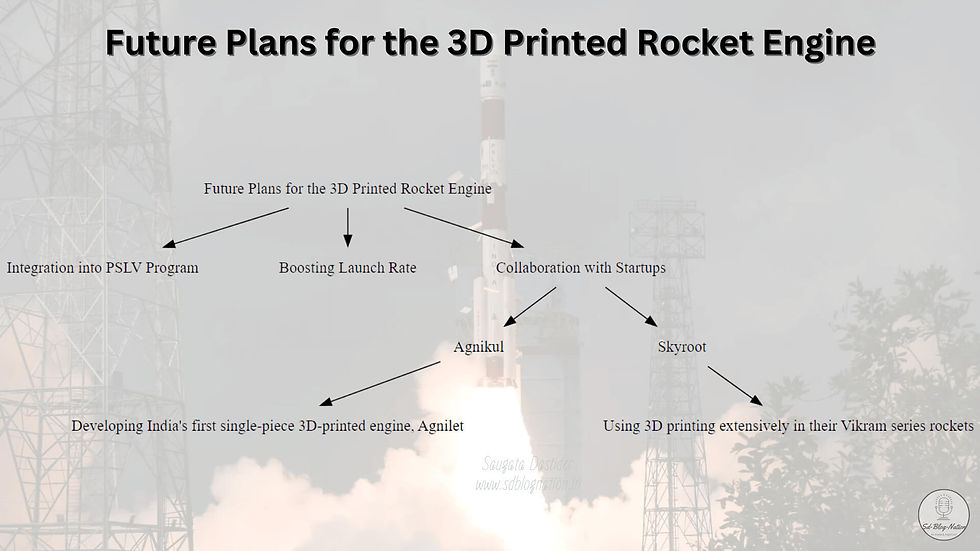
ISRO has significant plans for the future of the 3D printed rocket engine. Here are some key points:
Integration into PSLV Program: ISRO plans to integrate this advanced AM PS4 engine into its regular PSLV program. This signals a significant stride in rocket propulsion technology.
Boosting Launch Rate: The milestone with the 3D printed engine will help the country boost its launch rate. This is crucial as India has grand plans in human spaceflight including landing an astronaut on the moon and establishing a lunar base by 2047.
Collaboration with Startups: Indian startups like Agnikul and Skyroot are catching up in 3D-printed rocket technology. Agnikul is developing India's first single-piece 3D-printed engine, Agnilet, using a special high-performance alloy. Skyroot plans to use 3D printing extensively in their Vikram series rockets, aiming for frequent, low-cost launches. ISRO could potentially collaborate with these startups to further leverage 3D printing technology.
These future plans demonstrate ISRO's commitment to innovation and its dedication to advancing India's standing in space exploration and contributing significantly to the global scientific community.
Section 2: Contributions from AgniKul and Skyroot
2.1 AgniKul Cosmos Background and Achievements

AgniKul Cosmos, a pioneering Indian startup, is making significant strides in the space sector. founded in 2017, the company aims to democratize access to space by developing affordable and flexible launch solutions. AgniKul's vision is to make space accessible to everyone by reducing the cost and complexity of launching satellites.
Key Milestones and Current Projects
AgniKul's Cosmos primary launch vehicle is Agnibaan, a highly customizable, two-stage launch vehicle capable of delivering up to 300 kg payloads to orbits around 700 km high. Agnibaan can access both low and high inclination orbits and is designed for mobility, with the capability to launch from more than 10 launchports. The rocket uses LOX/Kerosene engines, with the number of engines on the first stage varying based on mission requirements.
AgniKul Cosmos is also developing the SubOrbital Technological Demonstrator (SOrTeD) mission, a single-stage launch vehicle powered by sub-cooled Liquid Oxygen (LOX) and Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF). This 6.2-meter-tall vehicle, equipped with four carbon composite fins for passive control, represents a critical step forward in demonstrating AgniKul's technological capabilities.
2.2 Skyroot Aerospace Background and Achievements
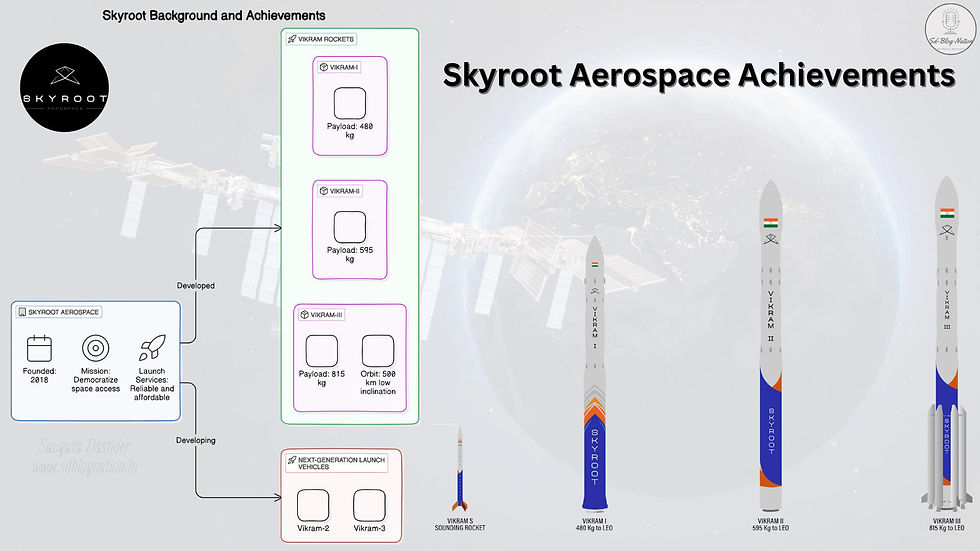
Skyroot Aerospace, founded in 2018 by former ISRO scientists, is another key player in India's private space sector. The company focuses on providing on-demand, cost-effective launch solutions for small satellites. Skyroot's mission is to democratize space access by offering reliable and affordable launch services.
Key Milestones and Current Projects
Skyroot has developed three versions of its Vikram rockets, named after Dr. Vikram Sarabhai, the father of the Indian space program. The Vikram-I can carry a 480 kg payload, Vikram-II can handle 595 kg, and Vikram-III can launch 815 kg to a 500 km low inclination orbit. These rockets are designed to offer quick and flexible launch options, making them ideal for the rapidly growing small satellite market.
Skyroot is also advancing with the development of next-generation launch vehicles, Vikram-2 and Vikram-3, which are set to enhance their launch capabilities further and support a wider range of missions.
2.3 Launch Vehicles: Details About Agnikul and Skyroot’s Launch Vehicles
Agnikul's Agnibaan and Skyroot's Vikram series rockets are at the forefront of India's private space launch capabilities. Agnibaan is known for its high degree of customization and flexibility, allowing it to serve a variety of mission profiles. It can be launched from multiple locations, enhancing its operational versatility.
Skyroot's Vikram rockets are modular and scalable, designed to cater to different payload capacities and mission requirements. These rockets emphasize rapid turnaround times and cost-efficiency, making them competitive options in the global small satellite launch market.
Contributions to India’s Space Missions
Both AgniKul and Skyroot are contributing significantly to India's space missions by providing innovative and cost-effective launch solutions. Their efforts align with ISRO's goals of increasing the frequency and reliability of satellite launches, supporting a wide range of applications from communication to earth observation and scientific research.
By leveraging advanced technologies such as 3D printing for engine components, both companies are setting new standards in the space industry. Their contributions not only enhance India's space capabilities but also position the country as a key player in the global space market.
Section 3: Applications and Future Plans of 3D Printing by ISRO

3.1 Current Applications: Other Areas Where ISRO is Using 3D Printing
ISRO has been actively exploring the use of 3D printing in various areas of their space missions. Here are some of the applications:
Spacecraft Components: ISRO has started incorporating 3D-printed components in spacecraft in small volumes. This includes parts that require complex geometries and high precision, which are challenging to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
Rocket Labs: Various units across ISRO, including rocket labs, are utilizing 3D-printed products to enhance the efficiency and performance of their technologies.
Deep Space Missions: ISRO's deep space missions are also leveraging 3D-printed components, which can significantly reduce weight and improve structural integrity.
PS4 Engine: ISRO has successfully tested a 3D-printed liquid rocket engine, known as the PS4. This engine has been redesigned using additive manufacturing to enhance efficiency and reduce the number of components from 14 to a single piece, eliminating 19 weld joints and significantly cutting down raw material usage and production time.
Specific Projects Where 3D Printing Has Been Successful
The advantages of using 3D printing in the PS4 engine include:
Reduction in Parts: The number of parts in the engine was reduced from 14 to a single piece.
Elimination of Weld Joints: 19 weld joints were eliminated, enhancing the structural integrity and reliability of the engine.
Material Savings: There was a significant saving in raw material usage per engine.
Time Efficiency: Overall production time was reduced by 60%.
These advancements indicate that ISRO is making significant strides in incorporating additive manufacturing techniques into its space exploration efforts. This technology not only enhances efficiency but also reduces costs and production time, paving the way for more advanced and reliable space missions.
3.2 Future Applications: Future Plans for 3D Printing in Space Exploration

ISRO has ambitious plans for the future application of 3D printing technology in space exploration. Here are some key areas of focus:
Lunar Habitats: ISRO is progressing with a working 3D printed model of a lunar habitat located in its lunar terrain test facility. This could play a crucial role in future plans for creating lunar outposts, providing a sustainable living environment for astronauts on the moon.
Collaboration with Startups: Indian startups like AgniKul and Skyroot are advancing in 3D-printed rocket technology. AgniKul is developing India's first single-piece 3D-printed engine, Agnilet, using a high-performance alloy. Skyroot plans to use 3D printing extensively in their Vikram series rockets, aiming for frequent, low-cost launches. ISRO could potentially collaborate with these startups to further leverage 3D printing technology.
Continued Development of 3D Printed Engines: ISRO plans to induct the 3D printed PS4 engine into the regular PSLV program, indicating a continued focus on developing and applying 3D printed engines in future missions.
Potential Advancements and Innovations
These advancements and future plans highlight ISRO's commitment to innovation and self-reliance in space technology. The integration of 3D printing technology not only enhances the efficiency of rocket production but also demonstrates the potential for future developments in space exploration. This includes the possibility of in-situ resource utilization, where materials found on celestial bodies like the moon or Mars could be used for 3D printing structures and components, reducing the need for material transport from Earth.
Section 4: Comparison and Challenges in Additive Manufacturing
4.1 ISRO vs. Other Space Agencies

Comparison of ISRO’s Advancements with Those of Other Space Agencies
ISRO has made significant strides in the field of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, marking a major advancement in India's space exploration efforts. Here’s how ISRO's achievements stack up against those of other major space agencies:
NASA: NASA has been at the forefront of 3D printing in space, using the technology for various applications, including producing spare parts and tools for the International Space Station (ISS). NASA is also advancing large-scale construction systems for building infrastructure on the Moon and Mars using 3D printing. They have funded numerous 3D printing projects for space exploration, demonstrating their commitment to leveraging this technology for long-duration space missions.
ESA (European Space Agency): ESA has been actively working on 3D printing projects, including perfecting the printing of space-quality metal components and launching the first metal 3D printer to the ISS. ESA collaborates with companies like Incus and Lithoz to develop and test 3D printing technology in microgravity using recycled powders from scrap metals available on the Moon, showcasing their innovative approach to sustainable space manufacturing.
SpaceX: SpaceX utilizes 3D printing in various parts of their machinery, including the SuperDraco thruster engine for the Dragon Spacecraft and components in the Falcon 9 rocket's engines. They also use 3D printing to produce astronaut helmets, highlighting the technology's versatility and efficiency in producing complex and customized parts.
Blue Origin: Blue Origin has partnered with Redwire to deploy 3D printing on an upcoming commercial space station, Orbital Reef. They use 3D printing in constructing their BE-4 rocket engine, emphasizing their focus on integrating advanced manufacturing techniques to enhance performance and reduce costs.
In conclusion, while ISRO has made significant advancements in additive manufacturing, other space agencies and companies are also actively exploring and implementing 3D printing in their operations. Each organization has its unique approach and focus, contributing to the overall progress in the field of additive manufacturing for space exploration.
Specific Successful Projects in Additive Manufacturing
ISRO’s PS4 Engine: The successful hot testing of the 3D-printed PS4 engine, which reduced the number of parts from 14 to a single piece and eliminated 19 weld joints, is a testament to ISRO’s capabilities in additive manufacturing.
NASA: Various 3D printing projects for the ISS and development of large-scale construction systems for the Moon and Mars.
ESA: Development of space-quality metal components and in-space testing of 3D printing using recycled materials.
SpaceX: Production of SuperDraco thruster engines and components for Falcon 9 rockets.
Blue Origin: Use of 3D printing in the BE-4 rocket engine and upcoming deployment in Orbital Reef.
4.2 Challenges in Large-Scale 3D Printing

Technical and Logistical Challenges in Large-Scale Construction Using 3D Printing
Large-scale construction using 3D printing presents several challenges. Here are some key ones:
Material-Related Challenges: The most cited challenges are material printability, buildability, and open time. These relate to the ability of the material to be printed, its structural integrity post-printing, and the time it remains workable during the printing process.
Scalability: Scaling up 3D printing processes to construct larger structures is a significant challenge. This includes ensuring the consistency and quality of the printed structures at a larger scale.
Structural Integrity: Ensuring the structural integrity of 3D printed buildings is a major concern. This includes the strength and durability of the printed materials and structures.
Lack of Codes and Regulations: The construction industry is heavily regulated, and many existing codes and regulations do not account for 3D printing processes. This can create legal and safety issues.
High Costs: The high cost of purchasing or renting 3D printing equipment and the logistics involved in getting these large 3D printers to the work site can be prohibitive.
Labor Shortage: There is a shortage of skilled labor that is trained in 3D printing technologies.
Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality in 3D printed structures is a challenge, especially given the relatively new nature of the technology in the construction industry.
How ISRO is Addressing These Challenges

ISRO is actively addressing these challenges through various initiatives and strategies:
Research and Development: ISRO is investing in R&D to enhance the material properties and printability of 3D printed components, ensuring they meet the stringent requirements of space missions.
Collaboration with Industry: By collaborating with industry leaders like Wipro 3D and startups like AgniKul and Skyroot, ISRO is leveraging the expertise and innovations of the private sector to overcome technical and logistical hurdles.
Pilot Projects: ISRO is conducting pilot projects to test and refine 3D printing techniques for large-scale applications, such as the development of lunar habitats and other space infrastructure.
Training and Development: ISRO is focusing on training and development programs to build a skilled workforce capable of managing and operating advanced 3D printing technologies.
Quality Assurance: Implementing rigorous quality control measures to ensure the structural integrity and reliability of 3D printed components and structures.
These efforts demonstrate ISRO's commitment to overcoming the challenges associated with large-scale 3D printing and harnessing its potential to revolutionize space exploration and construction.
Section 5: Future Prospects and Developments in India

5.1 Recent Developments in 3D Printing Technology in India
India has seen significant advancements in 3D printing technology across various sectors. Here are some highlights:
Intech Additive Solutions: Launched its Large Format range of Metal 3D Printers, the ‘iFusion LF series’, marking a significant leap in metal additive manufacturing capabilities.
Wipro3D and HAL: Collaborated to develop a metal 3D printed aircraft engine component, showcasing the potential of additive manufacturing in the aerospace sector.
Divide By Zero: Secured a US Patent for its ‘Advanced Fusion Plastic Modeling’ 3D Printing Technology and exported India’s first-ever 3D printer to the United States.
Andhra Pradesh MedTech Zone (AMTZ): Developing artificial organs through 3D bioprinting, indicating the transformative impact of 3D printing in the healthcare sector.
Intech Additive Solutions: Bagged a $2 million order for its iFusion series of metal additive manufacturing systems.
India’s First 3D Printed House: Virtually inaugurated by the Finance Minister, demonstrating the application of 3D printing in construction.
AgniKul: Partnered with EOS to accelerate in-house 3D printing of rocket engines.
STPL3D: Launched a series of industrial-grade SLA 3D printers in India.
VIT Chennai and Sedaxis Advanced Materials: Established an Additive Manufacturing Centre of Excellence, fostering innovation and research in 3D printing.
These developments indicate that the Indian 3D printing industry is growing rapidly, with advancements in aerospace, healthcare, construction, and other sectors. The market revenue surged to $111.0 million in 2022 and is expected to reach an estimated $705.1 million by 2030. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of 3D printing technologies across materials, evolving from prototyping to end-use production, with metal additive manufacturing leading the course.
5.2 Future Scopes and Projects
Upcoming Projects Involving 3D Printing in Space Exploration
ISRO: ISRO has successfully tested a 3D-printed liquid rocket engine, marking a major advancement in India's space exploration efforts. The engine is planned to be inducted into the regular PSLV program, indicating ISRO's ongoing commitment to integrating 3D printing technology into future missions.
AgniKul Cosmos: This Spacetech startup is building made-in-India 3D printed rocket engines. They are developing a higher stage semi-cryogenic liquid propulsion engine called Agnilet to support the orbital-class launch vehicle Agnibaan.
Applications of 3D Printing in Other Industries in India
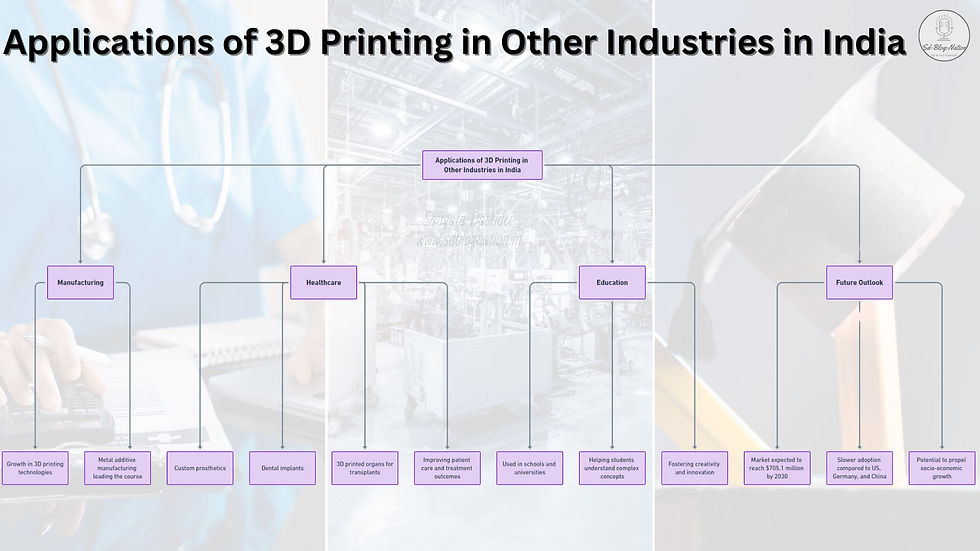
Manufacturing: The use of 3D printing technologies has grown in the country, with metal additive manufacturing leading the course. Companies like STPL3D have noted a growing demand for 3D printers in India.
Healthcare: 3D printing is being used to create custom prosthetics, dental implants, and even 3D printed organs for transplants. This technology can significantly improve patient care and treatment outcomes.
Education: 3D printing is being used in schools and universities to help students better understand complex concepts and to foster creativity and innovation.
The future of 3D printing in India looks promising, with the market expected to reach an estimated $705.1 million by 2030. However, the adoption of 3D printing technologies in India has been slower compared to countries like the US, Germany, and China. Nonetheless, the potential of additive manufacturing to propel socio-economic growth has caught the attention of the Indian manufacturing ecosystem.
Conclusion
ISRO's remarkable achievements in recent years, from the successful landing of Chandrayaan 3.0 near the moon's south pole to the ambitious Aditya L1 Solar Mission and the pioneering Gaganyaan crewed space journey, highlight India's growing prowess in space exploration. The organization's dedication to innovation is further demonstrated by the groundbreaking development and testing of the 3D printed PS4 rocket engine, which promises to revolutionize rocket manufacturing with enhanced efficiency and reduced costs.
The advancements in 3D printing technology, particularly in the aerospace sector, are a testament to India's commitment to self-reliance and technological excellence under the Atmanirbhar Bharat mission. With contributions from Indian startups like AgniKul and Skyroot, the country's space industry is rapidly evolving, showcasing significant strides in additive manufacturing and its applications in space missions.
As India continues to enhance its capabilities in space technology and 3D printing, the future looks promising. The integration of advanced manufacturing techniques not only boosts the efficiency of space missions but also opens up new possibilities for sustainable and cost-effective exploration.
For a comprehensive understanding of ISRO’s recent milestones, we encourage you to read our previous articles on:
These articles provide detailed insights into the incredible achievements of ISRO and the exciting future of space exploration in India. Visit our website at www.sdblognation.in to read more and stay updated with the latest advancements.
Reference
ISRO Successfully Tests 3D Printed Rocket Engine, Made by Wipro's 3D Printing Biz Unit.
India’s first private rocket, engine and satellite signal an Aatmanirbhar success story.
ISRO tests ‘Made-in-India’ 3D-printed rocket engine. What is it?.
ISRO Chief Articulates Vision That Underscores Private Space Sector.
ISRO and Social Alpha join hands to establish SpaceTech Innovation Network (SpIN).
What is a 3D-printed rocket engine? 7 points to know after successful ISRO test.
ISRO successfully tests 3D-printed rocket engine: What is 3D printing.
ISRO tests ‘Made-in-India’ 3D-printed rocket engine. What is it?.
Isro achieves major milestone with 3D printed rocket engine.
ISRO Successfully Tests 3D-Printed Liquid Rocket Engine for 665 Seconds.
ISRO achieves major milestone with 3D printed rocket engine test.
With 3D-printed rocket engine, Isro adds another feather to cap.
ISRO successfully conducts long-duration hot tests of Additive Manufacturing.
India’s 3D-printed rocket engine aces long-duration hot testing.
ISRO reaches milestone with successful long-duration test of 3D-printed rocket engine.
ISRO successfully tests 3D-printed rocket engine - Onmanorama.
ISRO Tests Redesigned 3D Printed Rocket Engine - 3D Printing.
India makes breakthrough by test-firing new 3D-printed rocket engine.
How does ISRO's 3D-printed rocket compare with other international 3D rockets?.
ISRO successfully tests 3D-printed rocket engine: What is 3D printing?.
How Agnikul's two-minute-long mission could give India a new launch vehicle.
Agnikul 3D-printed engine: Space-tech startup Agnikul to flight test 3D.
ISRO: India is slowly catching up with the world to use 3D printing in.
ISRO successfully tests 3D-printed rocket engine: What is 3D printing.
ISRO Achieves A Milestone With Successful Long-Duration Test Of 3D-Printed Rocket Engine.
How does ISRO's 3D-printed rocket compare with other international 3D rockets.
ISRO tests ‘Made-in-India’ 3D-printed rocket engine. What is it?.
ISRO Using Simulated Soil and 3D Printing to Construct Lunar Habitats.
How does ISRO's 3D-printed rocket compare with other international 3D.
How Does ISRO's 3D-Printed Rocket Compare With Other International 3D.
ISRO tests ‘Made-in-India’ 3D-printed rocket engine. What is it?.
ISRO successfully tests 3D-printed rocket engine: What is 3D printing.
How Does ISRO's 3D-Printed Rocket Compare With Other International 3D.
How does ISRO's 3D-printed rocket compare with other international 3D rockets.
Solving the Challenges of Long Duration Space Flight with 3D Printing.
NASA Looks to Advance 3D Printing Construction Systems for the Moon and Mars.
NASA Funds 3D Printing Projects for Upcoming Era of Space Exploration.
New NASA Funding Ignites 25 3D Printing Projects in Space Exploration.
ESA launches first metal 3D printer to ISS - European Space Agency.
SpaceX Reveals 3D-Printed Rocket Engine Parts - Design News.
Easing the way to the stars: 3D Printing in Space - Orbital Today.
Redwire 3D printing to be deployed onboard Blue Origin's pioneering Orbital Reef.
Blue Origin and Aerojet Rocketdyne to Push NASA's Space Exploration with 3D Printing.
A critical review of 3D printing in construction: benefits, challenges.
3D Printing in Construction: Growth, Benefits, and Challenges - Autodesk.
Propelling the widespread adoption of large-scale 3D printing - Nature.
Construction 3D Printing in India: Impact of Recent Developments.
India 3D Printing Market (2024-2030) Outlook | Growth, Industry.
India makes breakthrough by test-firing new 3D-printed rocket engine.
3D Printing in India: Tracing the Journey and Envisioning the Future.
Make3d.in - 3D Printer Manufacturer | 3D Printing Services | 3D Scanning Services.
3Ding | 3D Printers & 3D Printing Services, Hyderabad, India.
3D Printing in India: Slow Adoption & What the Future Holds.
100 3D printing experts predict the future of 3D printing in 2030.
Solving the Challenges of Long Duration Space Flight with 3D Printing.

















Comments